Customs Clearance of Electrical Insulators for High-Voltage Substations (HS 8546 + Documents & Standards)
For estimates of time and cost to clear electrical insulators (high-voltage substations), contact the Saba Tarkhis experts.
Instant Free Consultation1) Types of Electrical Insulators and Their Specialized Applications
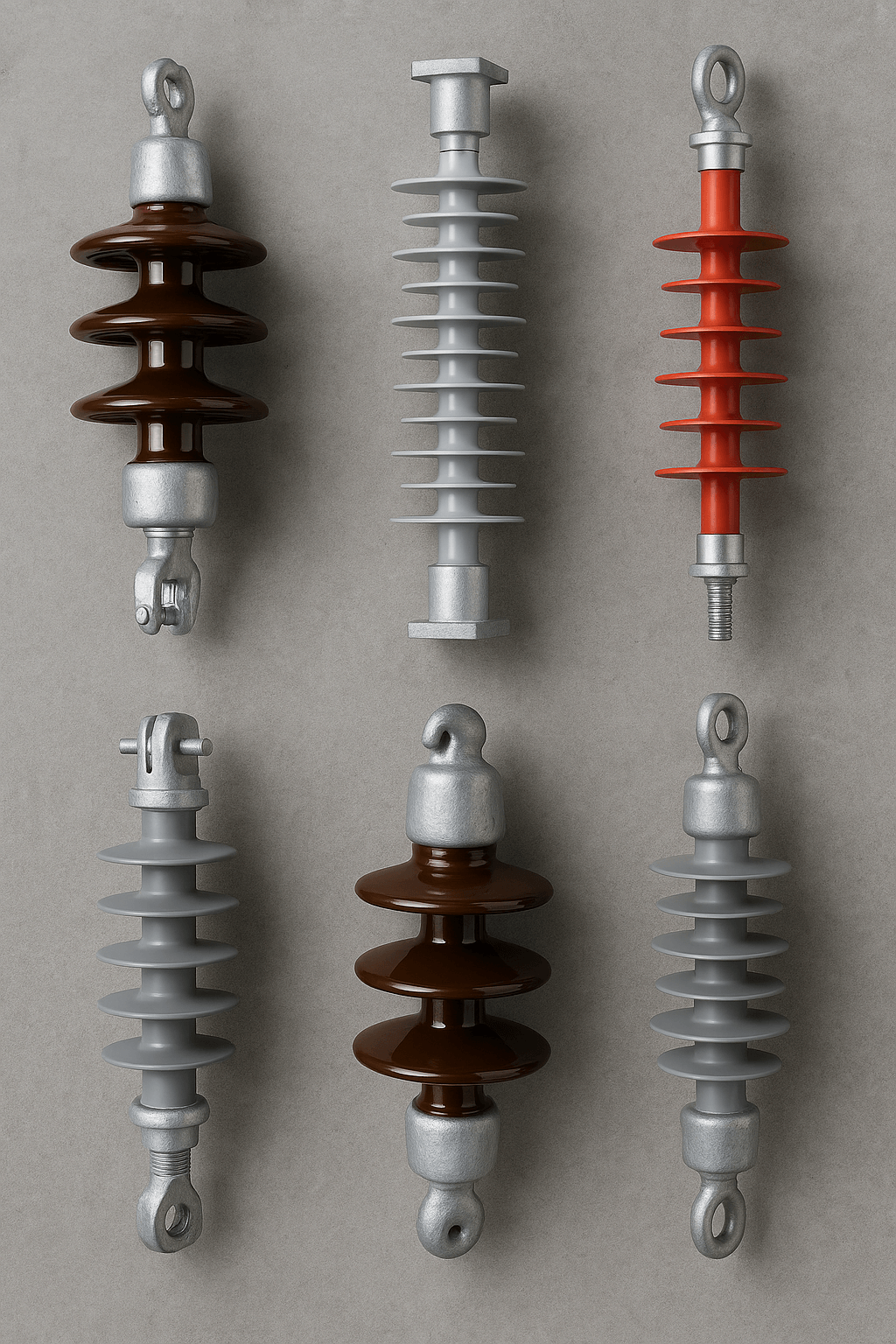
1. Pin Insulators
High mechanical strength: Designed to resist mechanical forces such as conductor weight and wind load.
Strong insulation: Typically made of high-quality ceramic/porcelain and offer good resistance to high voltages and harsh environmental conditions.
Applications: Widely used in urban and rural distribution and transmission lines.
2. Porcelain Insulators
High thermal resistance: Capable of withstanding very high temperatures.
Environmental resistance: Excellent stability against temperature changes, humidity, and weathering, with long service life due to strong physical and chemical integrity.
Applications: Suitable for high- and extra-high-voltage substations, particularly in harsh climates.
3. Glass Insulators
Transparency and visual inspection: Natural transparency makes changes and defects (such as cracks) easily visible.
Corrosion resistance: Stable against chemicals and corrosive agents, suitable for specific environments.
High electrical resistance: Able to withstand high voltages.
Applications: Widely used on high-voltage transmission lines, especially where visual inspection matters.
4. Composite Insulators
Pollution resistance: Due to special polymeric materials, they show greater resistance to environmental contaminants such as dust and industrial fumes.
Low weight: Lighter than porcelain and glass types, helping reduce installation and transport costs.
High flexibility: Composite structure provides better flexibility against impact and mechanical stress.
Long service life: Resistant to corrosion and harsh conditions, typically lasting longer than other types.
Applications: Widely used on high- and extra-high-voltage transmission lines, particularly in polluted and harsh environments.
2) Import and Export Conditions for Electrical Insulators
3) Import/Export Volume and Global Role
4) Key Points for Clearing Electrical Insulators
1. Tariff Heading (HS Code)
2. Required Documents
3. Standards and Technical Compliance
4. Authenticity Verification and Quality Control
5. Practical Note
| Item | Short Description | HS Code |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical insulators (high-voltage substations) | Porcelain / glass / composite; transmission lines | 8546 |
Precise subheading depends on material, rated voltage, design (pin/suspension/post), manufacturing standard, and end use.
Need accurate HS classification, permits, and document preparation? Our team manages your case end-to-end.
Submit Proforma Request
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the HS code for electrical insulators?
In general, insulators fall under Chapter 85, heading 8546; the exact subheading depends on material, application, rated voltage, and manufacturing standard.
Which documents must be submitted for clearance?
Per your text: Commercial Invoice, Bill of Lading, Certificate of Origin, and test certificates from internationally accredited bodies. Depending on the case, ISIRI/IEC approvals may also be required.
Are special permits required for some types?
Yes. As noted, “clearance of certain items is subject to obtaining special permits.” Based on the project and technical specifications, additional inquiries with customs and relevant authorities are recommended.
What are common import origins for insulators?
According to your data: China, India, and several European countries. For Iran’s exports, destinations include Iraq, Afghanistan, and some Central Asian countries.
.png)
