Customs Clearance of Gluconic Acid (HS Code + Documents & Permits)
For accurate estimates of the clearance time and cost for gluconic acid (food/pharma/industrial grade), contact the Saba Tarkhis experts.
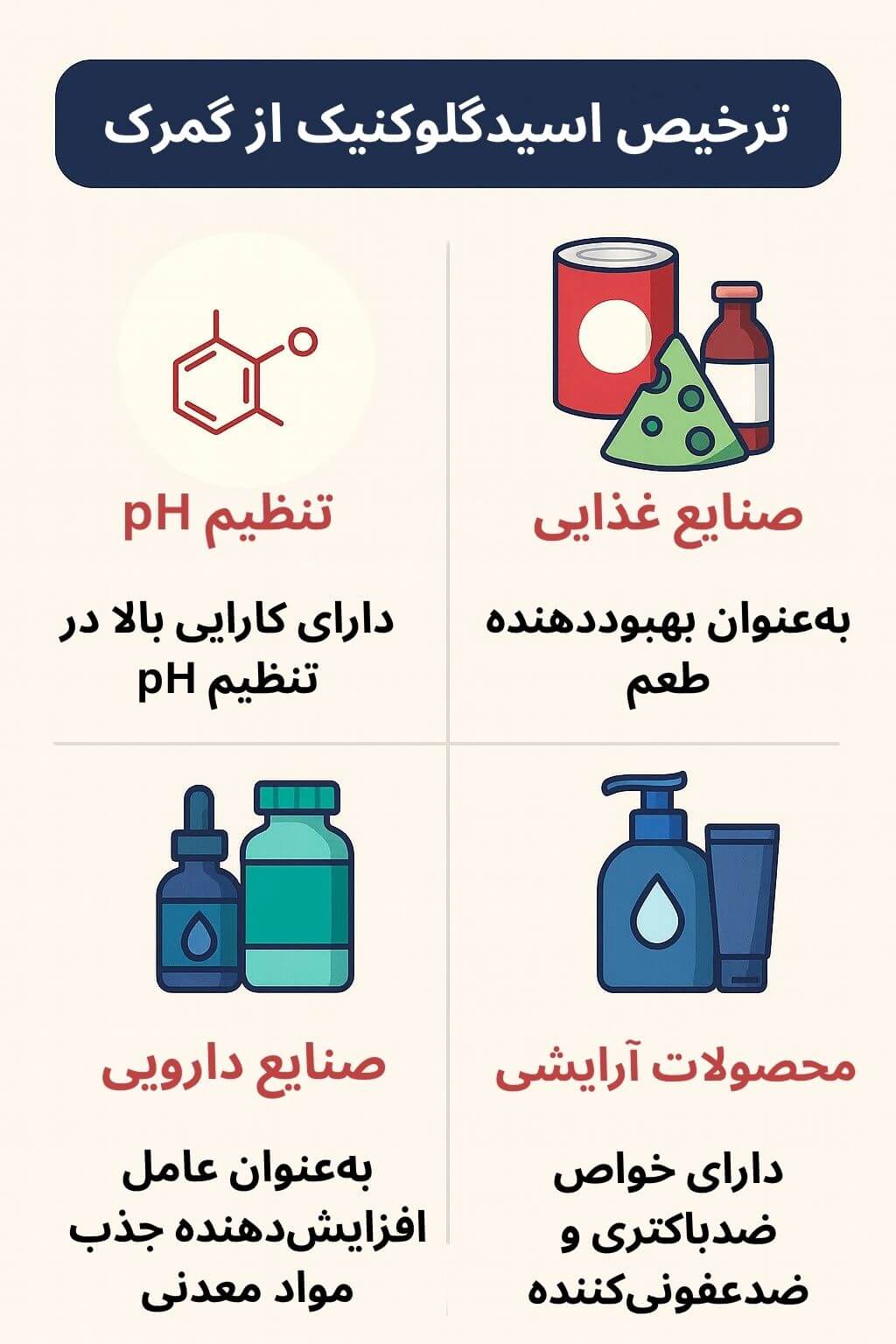
Instant & Free Consultation1) Specialized Applications of Gluconic Acid
2) Steps for Customs Clearance of Gluconic Acid
HS code and tariff
Import permits and standard approvals
Order registration in the National Trade System
Submission of transport documents
Customs and standards inspections
Need precise HS classification, health/standards permits, and document prep? Our team manages the entire case end-to-end.
Request a Proforma Quote3) Special Conditions for Import & Export of Gluconic Acid
Countries exporting to Iran
Countries importing from Iran
Global trade volume of gluconic acid
Leading global exporters
Major global importers
4) Required Documents for Clearance of Gluconic Acid
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the HS Code of gluconic acid?
Per your text, the customs tariff code for gluconic acid is 29181600 and is the basis for duty calculation and customs declaration.
What permits are required for import as a food additive?
Ministry of Health and Food & Drug Organization approvals are mandatory; compliance with international quality standards must be verified.
What are the key points for order registration?
Weight, volume, packaging type, and value must exactly match the invoice and packing list when entered into the National Trade System to prevent delays.
Who are the main suppliers for Iran’s imports?
Based on the text, China, India, and several European countries are the main sources of gluconic acid for Iran.
Saba’s Specialized Services for Gluconic Acid Clearance
.png)
